Equilibrium Price
Why does the price change? For example, the 64GB iPhone XR price was $749 in 2018, but it is now $499 in 2020. Before you know how price changes, it is essential to understand what consumers and producers mean.
The consumer is an individual who pays some amount of money to consume goods and services. For example, people who are shopping in a shopping mall are considered consumers. The producer is someone who creates and supplies goods or services. For example, companies like Nike and Apple are producers. Price constantly changes because consumers want to buy things that they want at lower costs, and producers want to sell their products at higher prices to earn more money. In 2020, demand for iPhone XR is lower than the demand in 2018 because newer phones have come out which means that fewer people want iPhone XR. Accordingly, Apple decides to lower the price of the iPhone XR to sell more products.
The price where many consumers are willing to buy and many producers are willing to sell is called an equilibrium price. The market is efficient at this price because the optimal amount of iPhone XR is being produced and consumed. At this price, both consumers and producers are happy.
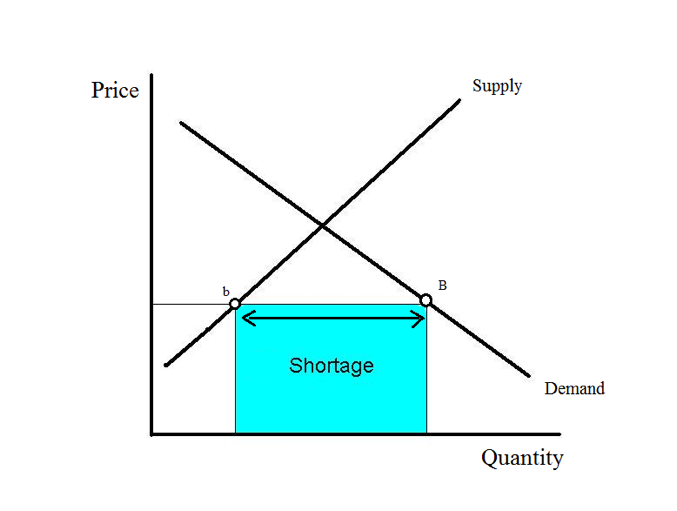
However, not everything is sold at the equilibrium price. What happens when demand is greater than supply? Let’s say that iPhone 13 is introduced at a price of $1200 in the future, and everyone is eager to buy iPhone 13. In this situation, shortage will occur.
At a price of $1200, Apple is willing to sell only 1,000 iPhone 13. On the other hand, 1,500 people are willing to buy an iPhone 13. Some people are even thinking of paying $1500 to buy iPhone 13. In this situation, Apple will raise the price of the iPhone 13. As a result, the price will arrive at the equilibrium price.